The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a consumption tax that’s charged on most goods and services in New Zealand. It’s called a consumption tax because it’s levied on things we “consume” (figuratively as well as literally), rather than being levied on our income.
If you’ve ever really studied a receipt, say from like a large, orange hardware store, you’d no doubt have noticed that extra dollar amount at the bottom of your receipt marked “GST”.
GST is 15% flat tax levied on top of whatever you paid for your lawn mower/DIY terrarium kit/gnome lawn ornament. But it’s not profit kept by the retailer – instead, it’s collected by them on behalf of the IRD.
If you’re a sole trader, you may have wondered if you’re supposed to be charging GST too. And if so, how do you do it? Why do you do it? Do you have to raise your prices to cover it? What if your clients are based overseas, do they still have to pay GST as well?
All great questions. Luckily, we’ve got the answers. Let’s dig in.
1. Introduction to GST
What is GST?
Like we mentioned earlier, GST is a consumption tax levied on things we consume. We’re not just talking about food and drink here though; a consumption tax applies to most resources (goods and services) that can be used up, or “consumed”.
GST is also a flat tax (unlike income tax, which is a progressive tax system). This means that the GST tax rate – 15% – doesn’t change, no matter how much you earn, what you buy, or how much it costs.
(Unless the product you’re selling is zero-rated – more on this later).
If you make $60,000 or more in business income, you’re required to register for and charge GST (see below). This means that you charge an additional 15% on top of your regular fees, which you record and pay to the government when you file your next GST return.

Whenever you buy goods and services for your business that have GST added, you can subtract the cost of the GST you’ve paid from the GST you need to pay the government. If you’ve paid more GST than you’ve collected, you may be eligible for a GST refund.
Not everything you can purchase is subject to 15% GST, however. The New Zealand government exempts certain goods and services from GST, including long-term rental housing, donated goods, financial services, and (weirdly) fine metal.
Other goods and services are “zero-rated”, meaning they have a GST rate of 0%. For more information, and for a full list of these goods and services, you can visit the IRD website.
Do I have to register for/charge GST?
Short answer
- If you’re registered for GST, you must charge and collect GST.
- Sole traders and businesses who make over $60,000 in self-employed income in any given 12-month period have to register for GST.
Long answer
If you make less than $60k in self-employed income
If you’ve made less than $60k in the last 12 months, you don’t have to register for GST. You can if you want to, but like with any business decision, there are pros and cons.
The main benefit of being GST registered is that you can claim back GST on your business expenses. If you pay more in GST when buying supplies for your business than you charge your clients, you are eligible for a GST refund.
If you’re below the threshold you may decide that registering for GST isn’t worth it, as it can be a lot of extra paperwork for little reward. And as sole traders, ain’t nobody got time for that.
There are a few cases, however, in which you may consider registering for GST while you’re still under the threshold. If you buy a lot of supplies in bulk for your business, for example, then being able to claim the GST back can help you better manage your cash flow. Similarly, it might make it easier to deal with your suppliers.
Whether or not you register for GST is up to you, but think of it as a calculated business decision. If you’re under the threshold, you need to decide if the benefits outweigh the cons.
Registering for GST: pros and cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
If you make $60k+ in self-employed income
If you’re a sole trader and you earn $60k a year of self-employed income, you are required to register for and charge GST on your goods and services. Yes, even if you aren’t registered as a company, or don’t have an NZBN – neither are necessary for GST registration.
If you’re an employee with a sole-trader side hustle, you only have to register for GST once your side-hustle income reaches $60k. Your combined income doesn’t count towards the threshold.
It’s also important to note that the $60k threshold doesn’t apply to a single financial year, but rather any 12 months in succession.
For example, if you make $60k between June of one year and July the next, you’re required to start charging GST immediately – even though that 12 month period is split between two financial years.
2. Registering for GST
It’s a common misconception that registering as a sole trader, filing a self-employed tax return, or applying for an NZBN, automatically registers you for GST. This isn’t the case.
If you haven’t specifically registered for GST, you are not registered for GST. You won’t have to charge GST, and you can’t apply for GST refunds.
If you have registered for GST, even if you aren’t required to, or you aren’t over the $60k threshold, you must collect and pay GST. The amount of GST you’ll need to pay is based on the income you receive during that GST period. You need to make sure that you collect GST from your clients, otherwise you’ll have to go back and ask your clients to retrospectively pay for GST, or pay your GST bill out of pocket (!!!).
Registering for GST is fairly straightforward. If you need a hand, check out our guide to registering for GST, which walks you through the process.
💡 If you’re GST registered, you’ll also have to provide your clients with “taxable supply information’’, which has to meet specific requirements. For more information, check out our ultimate guide to invoicing.
🙋 If you’re a Hnry user, we’ll let you know when you start approaching the $60k GST threshold. Plus, once you’re registered, we’ll automatically sort your GST, and file all your GST returns for you.
Tl;dr
- Unless you’ve registered yourself for GST, you are not GST registered.
- If you are GST registered, you must charge GST.
- If you make over $60k in any given 12-month period, you will need to register for GST.
- You’ll need to collect GST once you’re GST registered.
GST Periods
When you register for GST, you decide how often you would like to file GST returns. This timeframe then becomes your GST period
There are three options you can choose from:
- Monthly
- Easier to keep track of, but involves more paperwork
- Bimonthly (every two months)
- 6-monthly (only an option if you earn less than $500,000 a year)
- Harder to keep track of (if you don’t use Hnry), but less paperwork overall
You’ll also decide whether you’ll pay on a “payments” or an “invoices” schedule.
(FYI at Hnry, we work on a payments basis).
Sometimes, you may find that within a GST period, you’ve paid more in GST than you have collected. In these instances, you would receive a GST refund from IRD.
“Payments” vs. “Invoice” schedule
When you register for GST, you’ll need to decide whether to register on a ‘payments’ or ‘invoice’ basis. Basically, will you pay GST when you’ve invoiced it? Or will you pay GST after you’ve received the payment of your invoice?
It’s an important choice, and will affect your business’ cash flow. Let’s break down the pros and cons.
Payments Basis
When you register for GST on a payments basis, the date that you recognise the GST on your sales will be the date that you receive the money.
For example, if you send someone an invoice on the 20th of February, and they pay you (including GST) on the 20th of March, you wouldn’t declare it to the IRD until after you’ve been paid – even if your GST period ends at the end of February.
Instead, you’d count it as part of the next GST period, at which point you’d send it to the IRD.
Invoice Basis
When you register for GST on an invoice basis, the date that you recognise the GST on your sales will be the date included in the invoice to your client.
Using the same example, you send an invoice on the 20th of February, and they pay it on the 20th of March. On an invoice schedule, you’d have to declare the GST in the period the invoice was dated, and pay that GST to the IRD – even if you haven’t received it from your client yet.
There are some benefits to an invoice schedule for registered companies, but for sole traders, it can get stressful. Especially if your clients are notoriously late in paying their invoices.
There may also be more paperwork involved. Heads up.
Cancelling your GST registration
If your earnings drop below $60k in a 12 month period, or if you registered for GST while under the earnings threshold, and you decide that you no longer want to be GST registered, you can always cancel your GST registration.
The process is fairly straightforward. All you have to do is:
- Login to myIR
- Navigate to your GST account
- Select “More…”
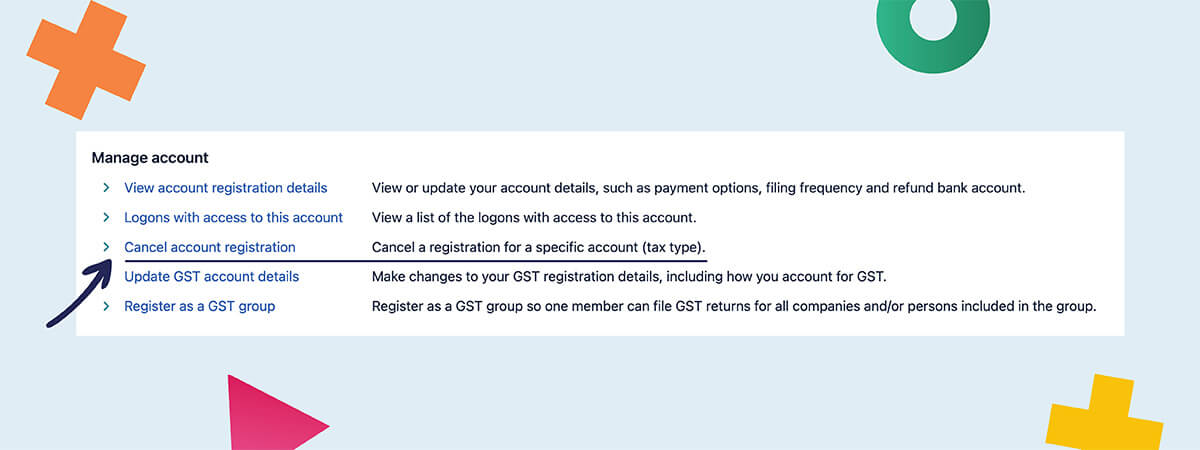
- Select “Cancel account registration”
- Follow the prompts to cancel your GST registration
Simple! Done! Whoohoo!
3. Charging and Collecting GST
If you’ve decided to register for GST, the next step is to actually collect GST from your customers. This means adding an additional 15% to your prices.
It can be a bit nerve-wracking to suddenly “raise your prices” by 15%. But customers are used to paying GST, and should understand that they’re not paying you extra – they’re paying tax they owe to the government.
Clients who are GST registered should be indifferent to you charging them GST, as they can claim it back in their own GST return. But if you’re worried about the price jump, you could preempt the change with a quick email to your regular clients.
You can also specify in your quotes whether or not your prices are GST inclusive or exclusive. The way you position it could make a real difference, depending on your customer base.
What we don’t recommend doing is absorbing the cost yourself – eg. not adding 15% GST to your prices, and paying your GST bill out of your own pocket. While the cost for your customers won’t change, you’ll effectively be taking a pay cut. And that will stack up over time in terms of revenue lost – especially if it means you have less left over to invest in your business.
Remember: GST is a tax levied on your customers, not you!
Calculating GST
GST is a flat tax of 15% added to most goods and services sold by someone who is registered for GST. To add GST, you divide the original price by 100, multiply that number by 15, and then add that number on to the original price:

The equation to subtract GST is slightly more complicated. What you do is take the original price, multiply that by 3, divide the result by 23, round to the nearest two decimal points, and then subtract that from the price:

It’s not intuitive, but it works.
GST inclusive vs. added GST
Whether a price is GST inclusive, or has GST added on top, makes a real difference to the final cost.
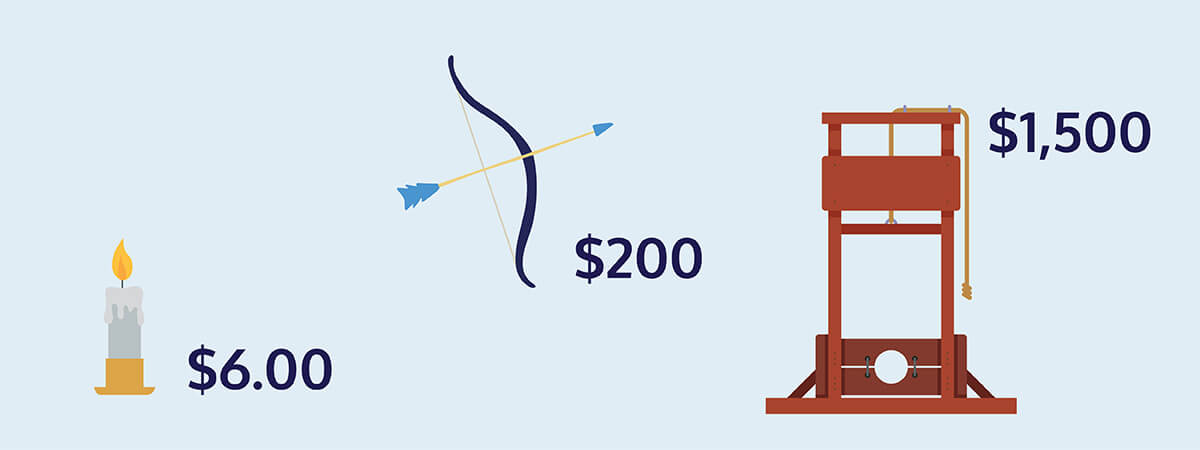
Say you go to a medieval fair and buy a beeswax candle for $6, a longbow for $200, and a life-sized, non-functional guillotine replica for $1500. You know, to decorate your living room.
If the price of each item was already GST inclusive, it means that 15% of the original price has already been calculated and added to the final cost:
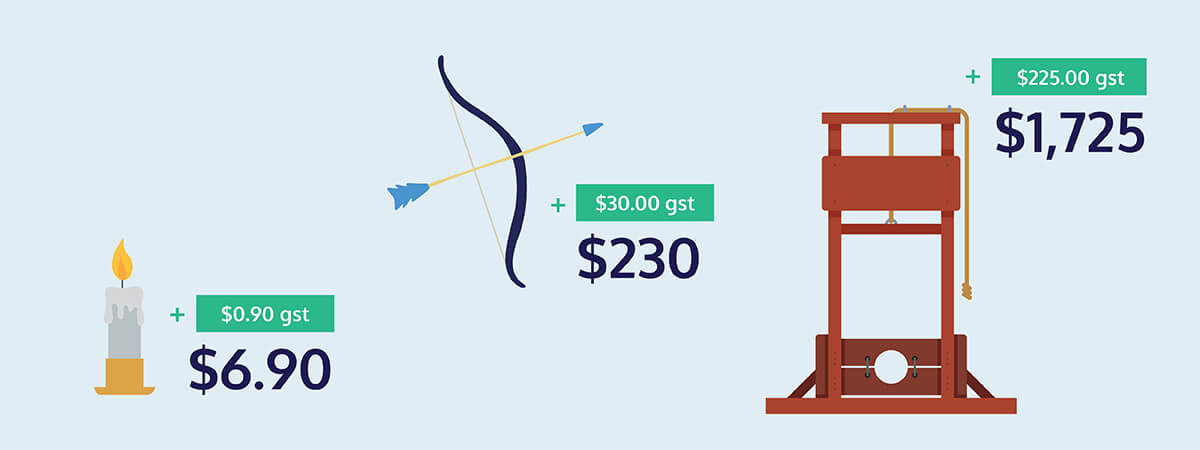
However, if each item still needed GST to be added on, the price would increase by 15%. What this means is that 15% of the original cost would be added to the final cost:
Moral of the story: Most vendors will let you know beforehand if they charge GST, but if you’re not sure, it’s worth it to check. You should also specify if your rates as a sole trader are GST inclusive or exclusive, just so there are no nasty surprises further down the track.
Also, you may want to ok a life-sized guillotine with your family before you bring it home and put it next to the TV. Just a thought.
GST Calculator
Recording GST on Invoices
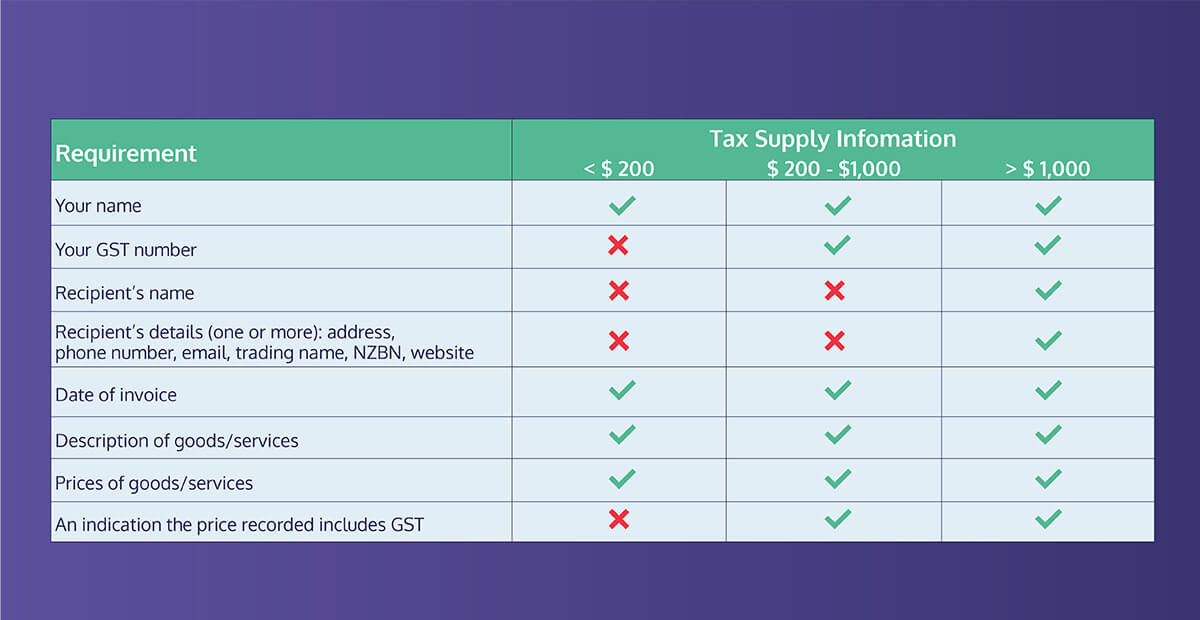
As of the 1st of April 2023, the IRD has introduced new, simplified rules for GST tax invoices.
If your invoice is for less than $200, it must include:
- Your name
- The date of the invoice
- A description of your goods/services
- The price of your goods/services
If your invoice is between $200 and $1,000, it must include:
- Everything mentioned above, as well as
- Your GST number
- An indication the price recorded includes GST
If your invoice is for more than $1,000, it must include:
- Everything mentioned above, as well as
- The recipient’s name
- The recipient’s address, phone number, email, trading name, NZBN, OR website
You may have also noticed that none of these invoices have to include the words “tax invoice”. That’s because they’re no longer considered tax invoices, but rather “taxable supply information”. Phew!
For those sole traders who invoice for smaller amounts, you could make your invoices even simpler by creating a separate document for clients containing the bits that don’t change – like your name, your registration number, your NZBN etc. That way, all that ever needs to be included in an invoice is the date, and a description of your products/services.
For sole traders invoicing at over $1k, you can’t simplify it – you’re basically still operating according to the old rules and requirements. Sorry team.
The good news is that these simplified invoicing rules also apply to claiming GST, as well as invoicing. So you know those frustrating clients who don’t always give you detailed invoices? If they’re invoicing you for under $200, you may now be able to claim GST without having to chase them up for more info.
Invoicing requirements table
FYI, Hnry users don’t need to worry about this rule change. Invoices sent through our app will still include all the information required under the old rules, so you’re covered no matter what.
We’ll also claim GST back for our users when we file their GST returns, so they don’t need to think about the maths and can get on with the fun stuff.
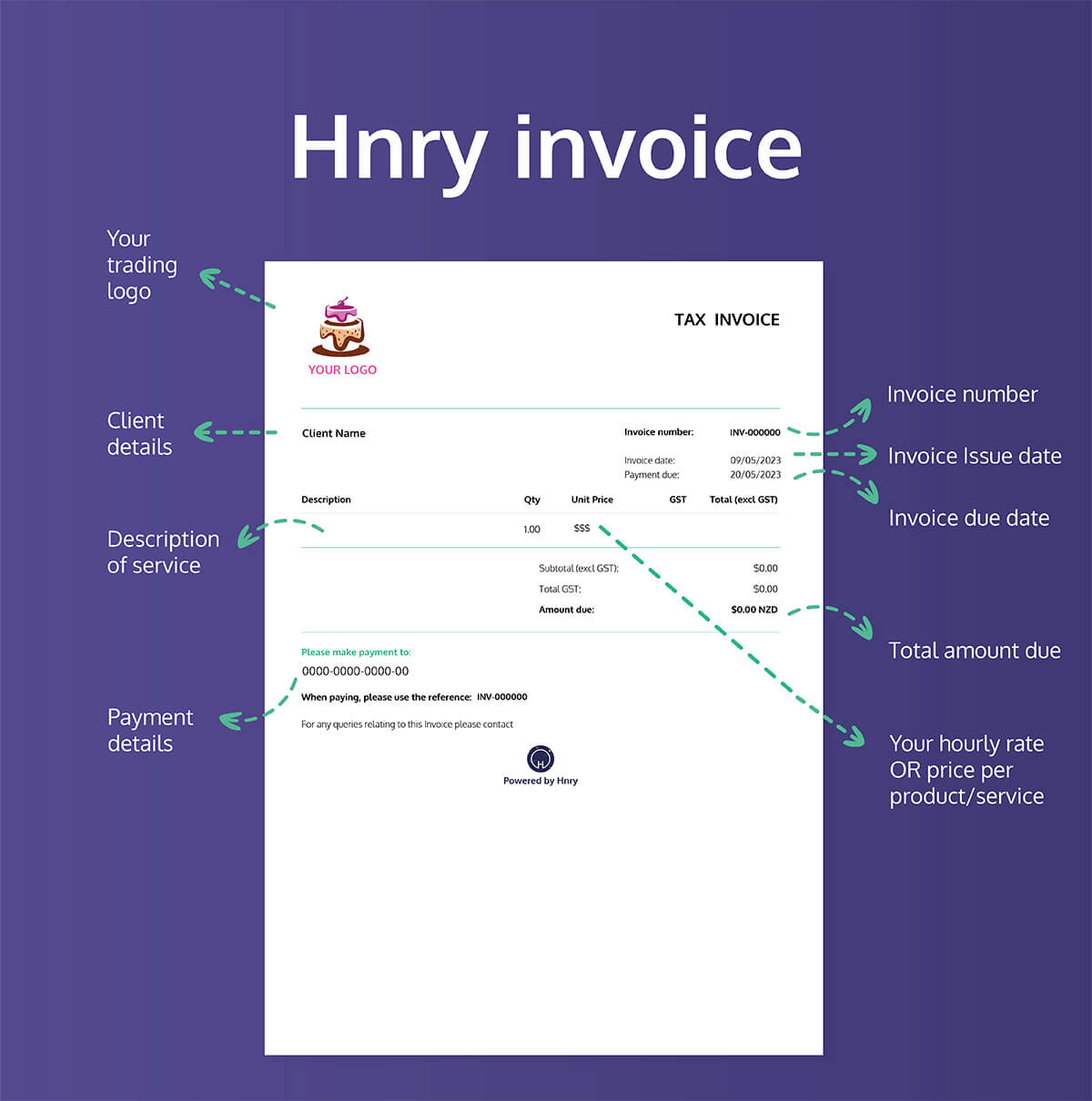
📖 Want to up your invoicing game? Check out our guide to invoicing like a pro
Charging/Paying GST overseas
Charging GST overseas
Whether or not you need to charge GST when selling your stuff overseas depends on whether or not your client exists in New Zealand.
By that, we mean whether or not they operate in, or have any trading presence in Aotearoa. We’re not trying to spark an existential crisis.
If your client operates outside of New Zealand, with no local presence, you generally charge them GST at a rate of 0% (this is referred to as being “zero-rated”).
While this seems illogical, there’s a difference between zero-rated and exempt.
- If you sell products that will be zero-rated, you’re still allowed to claim GST back from the IRD for any GST purchases you make.
- If you only sell products that are GST exempt, you’re actually not eligible to claim GST on business expenses. You shouldn’t be registered for GST.
So if you sell zero-rated products or services to an overseas client, you still need to record GST of $0.00 in your invoice. You’d include these sales in your regular GST returns. And you’re still eligible to claim back any GST you’ve paid for business expenses.
💡 Even if the product you’re supplying your client is zero-rated for GST, you still have to charge them GST – just at a rate of 0%. This means they pay nothing in GST, but you still have to record these sales in your regular GST returns. Yep, we know it’s weird and confusing – it’s just one of those things.
Paying GST overseas
Whether or not you pay GST on overseas purchases depends on who you’re buying from.
If an overseas business makes more than $60k NZD from low-value goods on New Zealand sales, they’ll be required to register for GST (are you sensing a theme here?).
They’ll then charge kiwi consumers 15% GST on top of their prices, to be passed on to the New Zealand government.
If an offshore supplier makes less than $60k NZD from New Zealand purchases, they’re not required to charge GST.
If you’re a GST-registered sole trader buying supplies for your business, your offshore supplier isn’t required to charge GST, even if they’re GST registered in their own country.
However, if you purchase something worth more than $1,000 NZD, New Zealand Customs Service will charge you GST, not your supplier.
Sounds confusing? Yeah, it is a bit. Basically, if you’re GST registered and you’re charged NZ GST, you can claim it in your GST return. If you’re not charged NZ GST, you don’t need to worry about it.
4. GST Returns
What is a GST return?
When you’re GST-registered, you are required to file GST returns on a regular basis.
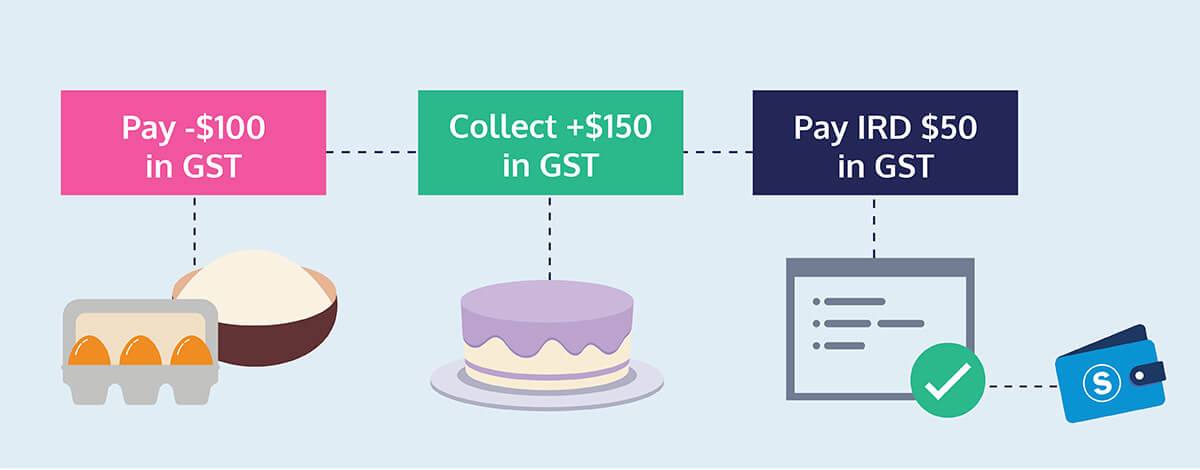
A GST return is essentially a declaration to the IRD of:
- the total GST you’ve collected on your sales/income; and
- the total GST you’ve paid while making business purchases.
What you then pay to the IRD is the balance between the two figures:
💡 Hold any GST you collect separately from the rest of your income. That way, you’ll always have the right amount on hand to send to the IRD. If not, you’ll be hit with fines and penalties.
🙋♀️ If you’re a Hnry customer, we do this on your behalf!
Whenever a GST period is complete, you’ll need to fill out a GST return. It can get slightly complicated, but the IRD walks you through the process on their website.
When are GST returns due?
Generally, GST returns are due on the 28th day of the month after the GST period ends.
For example, if you file 6-monthly and your GST period is from the 1st of December to the 31st of May, your GST return will be due on the 28th of June.
It’s a good idea to make a note of your GST return due dates and note them in your calendar. If you file late, you may end up with fines and penalties.
Alternatively, you could use Hnry. For just 1% +GST of your self-employed income (capped at $1,500 +GST a year), Hnry will calculate, pay, and file all your taxes for you. This includes filing all your GST returns. Whoohoo!
5. Tl;dr: GST Overview
Ok, we know that that’s a lot of information. To help it all stick, here’s the tl;dr:
- GST is a flat-rate tax of 15% levied on certain goods and services.
- You don’t need to register for GST if you’re a sole trader. If your income is below $60,000 in a 12 month period, registering for GST is optional.
- If you haven’t registered for GST, you’re not registered for GST. It’s not an automatic thing.
- You can be registered for GST as an individual sole trader – you don’t need to register a company, or even have an NZBN
- You can’t charge GST unless you’re registered for GST. If you’re registered for GST, you must charge GST (or get caught out by the IRD)
- If you register for GST partway through the year, you start charging GST from then on – you don’t have to back pay.
- GST returns are filed on a monthly, bimonthly, or 6-monthly basis.
Hnry will do it all for you. No, seriously.
You can read a 4000+ - word article on GST – or you can let us do it all for you instead.
(If you’ve made it this far though, we’re seriously impressed. Nerd.)
For just 1% +GST of your self-employed income, capped at $1500 +GST a year, Hnry will calculate and pay all your taxes, levies and whatnot for you, including:
- Income tax
- GST
- ACC levies
- Student loan repayments
- KiwiSaver contributions
We also file your income tax and GST returns for you, at no added cost. Plus, we can also handle all your financial admin, like:
- claiming expenses,
- sending quotes and invoices,
- and chasing up late-paying customers (politely of course.)
Basically, you don’t have to go at it alone anymore. Hnry was designed by sole traders, for sole traders. We know exactly what you need to get the job done.
Join Hnry today!